Cloud Computing Security

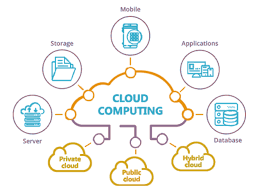
Cloud computing security or, more simply, cloud security refers to a broad set of policies, technologies, applications, and controls utilized to protect virtualized IP, data, applications, services, and the associated infrastructure of cloud computing. It is a sub-domain of computer security, network security, and, more broadly, information security. Security issues associated with the cloud Cloud computing and storage provide users with capabilities to store and process their data in third-party data centers. Organizations use the cloud in a variety of different service models (with acronyms such as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS) and deployment models (private, public, hybrid, and community). Security concerns associated with cloud computing are typically categorized in two ways: as security issues faced by cloud providers (organizations providing software-, platform-, or infrastructure-as-a-service via the cloud) and security issues faced by their customers (companies or organizations who ho...